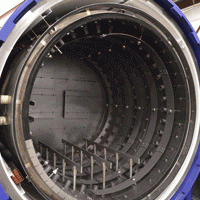
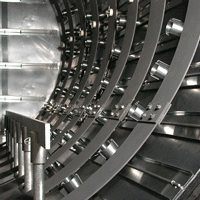
The heart of any vacuum furnace is said to be its hot zone and if properly constructed and well maintained will help ensure that the furnace performs in an optimal manner. One of the most important aspects of the hot zone is its insulation and the choice of materials used in its construction. In this article, we will focus on the two main Hot Zone configurations namely all-metal hot zones and carbon-based hot zones.
Thermal Insulating Systems: We begin, however, with a brief discussion of the three modes of heat transfer, namely convection, radiation, and conduction. To perform properly, the hot zone insulating system must contend with all three. In simplest terms, conduction and radiation may be thought of transferring energy to the surface of the part, while conduction is responsible for the heat to penetrate into the center of the parts. Conduction or conductive heat transfer occurs by direct molecular collision. On a microscopic scale, the kinetic energy of molecules varies in direct proportion to their temperature. So, as the temperature rises the molecules increase in motion and gain kinetic energy. They then collide with cooler surface molecules, transferring their kinetic energy and hence their heat, to the part surface.