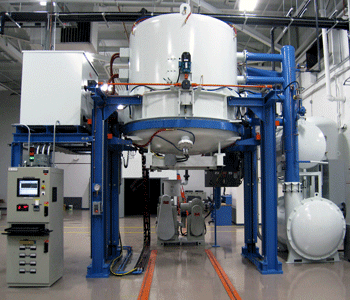
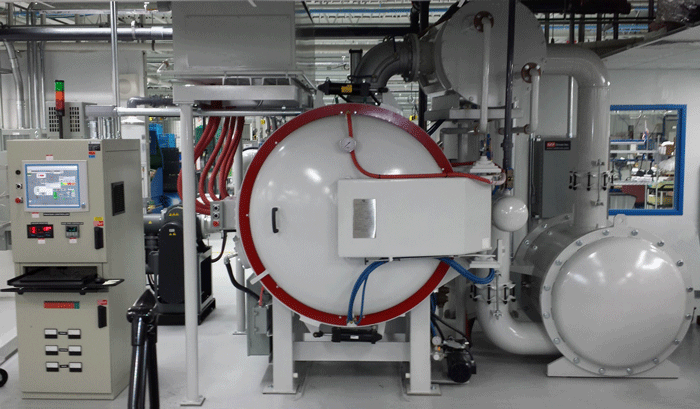
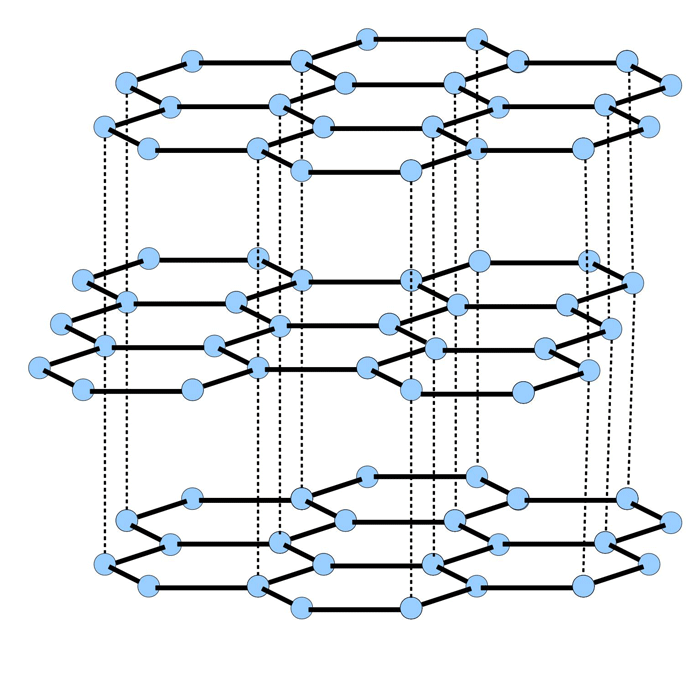
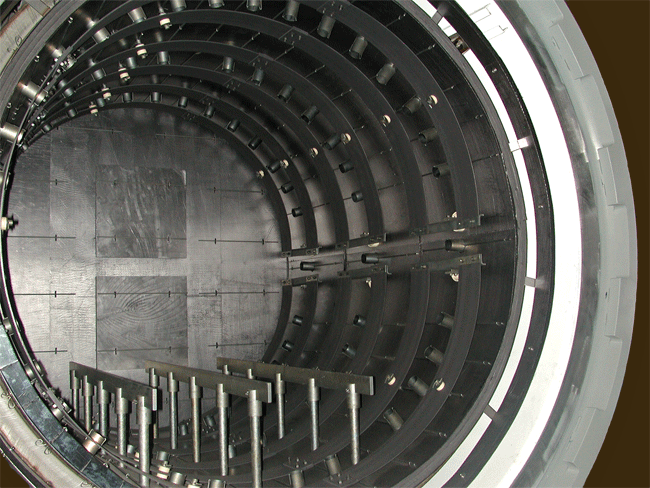
The role of materials science is to study, develop, design, and perform processes that transform raw materials into useful engineering products intended to improve the quality of our lives. It is said by many that material science is the foundation upon which today’s technology is based and that real-world applications would not be possible without the materials scientist. The discipline has expanded to encompass materials for many highly specialized product applications.
The industrial revolution thrust metals into the forefront of technology, and they have stayed there ever since becoming the very foundation on which our modern society is built. One cannot envision a life where our transportation and communications systems, buildings and infrastructure, industrial machines and tools, and safety/convenience devices that are not an integral part of our daily lives. Metallurgy is that part of materials science and materials engineering which studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, intermetallic compounds and their alloys. This definition is all-encompassing and includes the study of processes run in furnaces and ovens, the forging and rolling of metals, foundry operations, electrolytic refining, creation and use of metal powders, welding, heat treatment and much more. One might say that metallurgy is the application of knowledge of materials while materials science focuses on the theory of the structure, properties, processing, and performance of engineering materials.